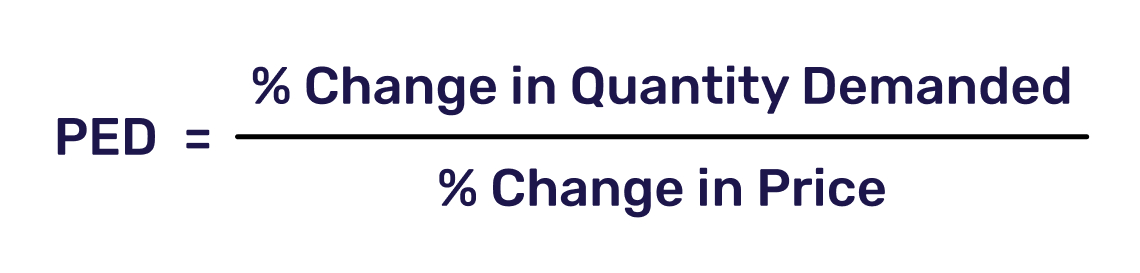Do You Believe in the “Magic” of Price Elasticities?
Price elasticity – advanced ML/AI price management feature that is a potential game-changer for retail businesses? Or, obscure “crystal ball” that doesn’t always work?
Price elasticities are indeed infinitely intricate and can be difficult to master. They have earned a well-deserved reputation on the retail market for being a powerful ML/AI weapon. Indeed, it is undeniable that the estimation of price elasticities can never be 100% accurate. However, they can deliver sufficiently accurate estimates to help save an extra 1-2% of retail margins through price elasticities alone (3-4% including all ML/AI features working with elasticities), and in the retail world this can translate to millions of dollars.
Whatever you may believe about price elasticities, what you definitely ought to believe in is the math and science underlying their function. You can also put belief into the skills of an effective Pricing Manager who knows how to make them work for your pricing strategy. After all, there is no crystal ball, and price elasticities are not actually obscure if the end-user understands what’s behind the figures they continuously render and adjust. Most importantly, you absolutely can get them under your control to generate brilliant results for your retail brand’s pricing strategy and overall margins.
Today, we will evaluate price elasticities in depth, with the purpose to debunk the mythology and mysticism behind them. This article aims to highlight price elasticities’ very logical and mathematical approach to refining prices, and the truly tangible benefits that come with them.
Price Elasticities Basics – What Do They Achieve?
Price elasticities use historical purchasing data to help retail professionals set optimal price ranges that benefit regular pricing and promotions. By definition in Economics, price elasticity measures the responsiveness of the quantity demanded or supplied of a good to a change in its price. Within the context of retail price management, price elasticities help businesses set and adjust prices based on past customer purchases and overall sales history, using this same mathematical formula as per its definition in the form of PED (we will get to this in greater detail later in this article).
In the end, as a retailer you can never lose sight of your customers – your loyal shoppers are the key to your business’s success. Their purchasing decisions, behavior as consumers, buying habits, and changes to any of these activities are what must drive your pricing strategy. In this sense, accurate price elasticities are your best pricing pal.
Under the Hood: The Inner Workings of Price Elasticities
It would be impossible to appreciate the true value of the price elasticities feature without establishing what’s behind the figures it renders. What factors, considerations, or events is each individual elasticity computed from? The quick and most immediate answer: Your customers’ wallets. Gathering sales history – every purchase, promotion, cross-sell, and everything in between both past and present – is the primary source of information from which price elasticity figures are rendered.
It’s also crucial to establish that when we say “price elasticities”, we are in fact referring to thousands upon thousands of SKUs that can be managed individually or in groupings like product families. In other words, each item can be its own elasticity, one single price that can flexibly fluctuate to serve your pricing strategy requisites. By using elasticities cleverly, pricing professionals are able to boost margins and optimally compete against other retail stores without damaging overall sales volume and business, all from one price elasticity feature that manages each individual SKU’s elasticity.
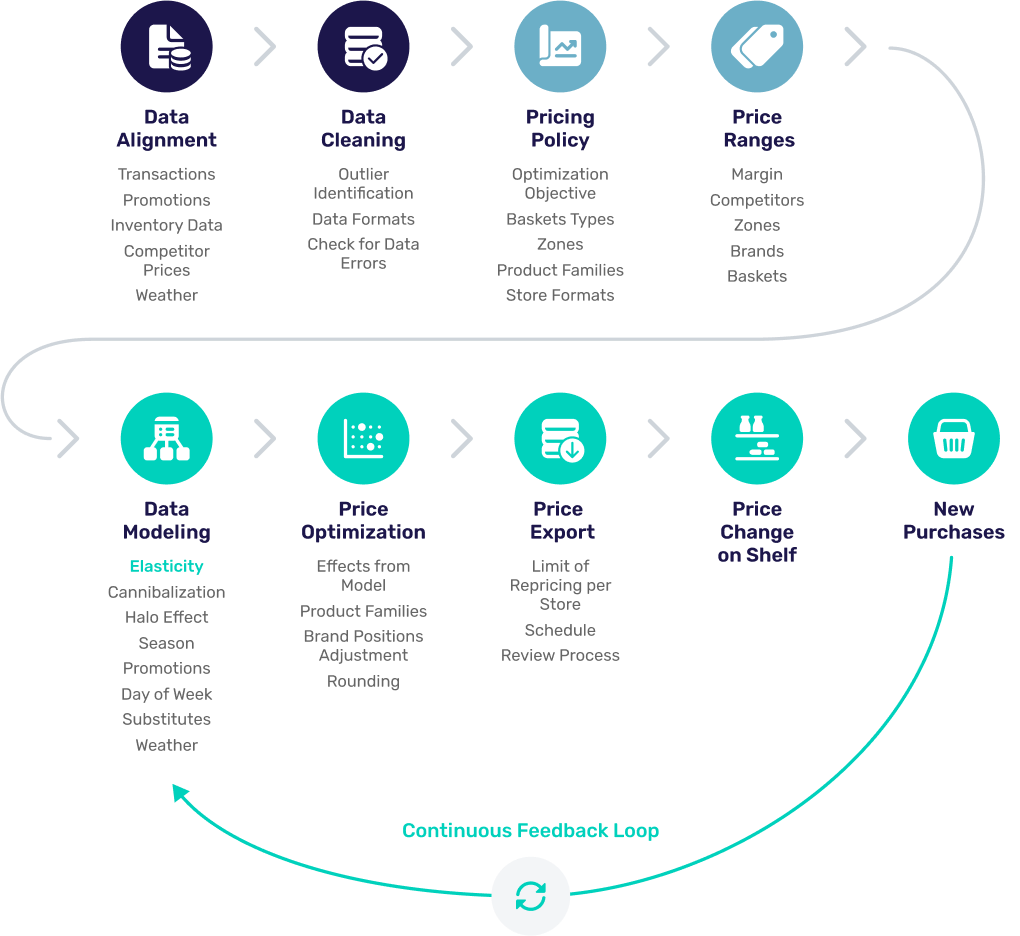
The graphic below is a step-by-step illustration of the overall processes occurring within Yieldigo’s price management engine, starting with data alignment and integration. Though there are various approaches to pricing, we can consider the model below to be an advanced approach to ML/AI pricing. You can see “Elasticity” highlighted here within the Data Modeling facet of the entire price management process.
Yieldigo Pricing Process Overview
Let’s now take a look at the six price management processes that remove mysticism from the price elasticity equation.
The 6 Price Management Processes that Debunk Mysticism Around Price Elasticities
1. Data Collection and Integration
Price Management software integrates various data sources to collect relevant information, such as:
- Historical Sales Data: Used to observe past pricing and sales volume.
- Market Data: Competitor prices, market trends, and economic indicators.
- Customer Data: Purchase history, preferences, and segmentation.
- External Data: Seasonal factors, events, weather, and other macroeconomic factors that can originate from data scraping tools or other data collection tools.
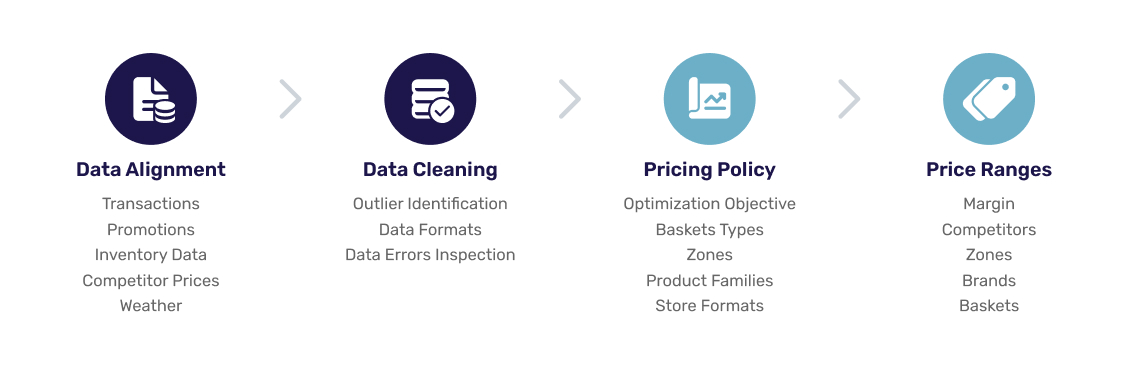
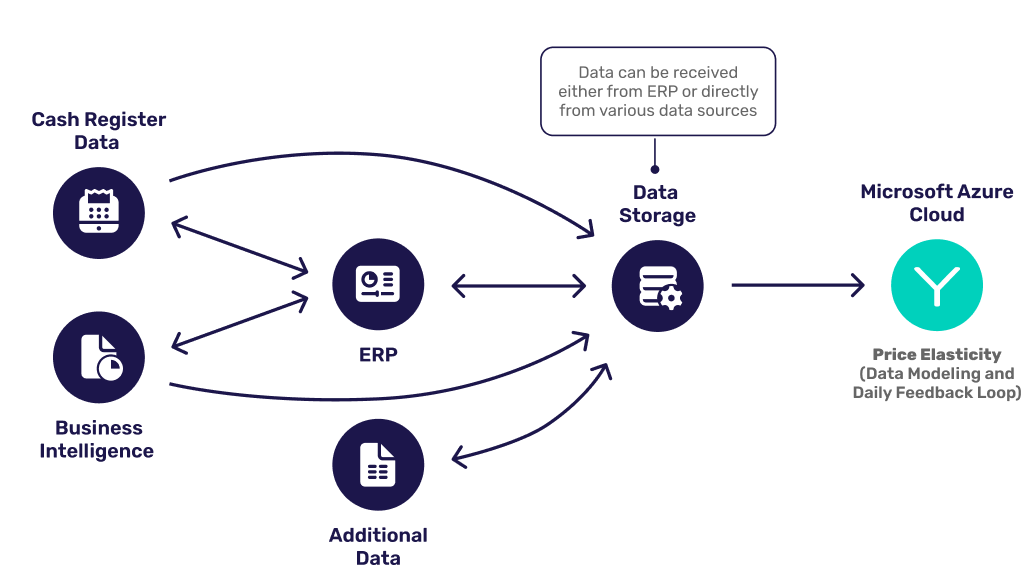
PART 1: Your Data
When looking at the pricing process graphic directly above, within the data alignment process there are several key inputs for your price elasticities, namely, your data. Data alignment is absolutely critical since transactions, promotions, inventory data, competitor prices, and weather, all play a crucial part in feeding the ML/AI engine with reliable data that a feature like price elasticities requires to deliver accurate and actionable pricing figures.
Every figure that your price elasticity estimates are based upon come from not one or two sources of business and customer data, but many. The data is coming in from your point of sale (POS) system, and is then being sent back to your price management software. This helps reinforce the ML/AI database in your price management software so that the new figures reflect the most recent customer purchases and behavior patterns.
Technically, figures can be broken down into hundreds of thousands of data sources if you consider each purchase to be a single data point. As such, price elasticities from up-to-date products are in fact based on hard data – your data – from your customers’ purchases, past and present.
Yieldigo’s Data Integration Process
Yieldigo’s product is built to integrate a retail organization’s data gold to weaponize it into actionable pricing strategy figures. Our implementation team helps to perform a successful data integration in unison with the end user’s pricing team. We clean their data to ensure that it is of good quality and accurate, which as we will see now is critical to delivering accurate price elasticity estimates.
Needless to say, the integration process is absolutely crucial. The expression you are what you eat absolutely applies to your price management software’s ability to calculate price elasticity in the most optimal way possible. The data that you feed into Yieldigo (or any ML/AI price management software, for that matter) renders the results you obtain, and therefore your internal data is the only limit to the elasticity figures you obtain.
2. Data Modeling (Demand Modeling)
Data modeling is a process that learns patterns of customer behavior. Using the collected data, the software creates a model of demand as a function of price and other variables. Advanced statistical techniques and machine learning algorithms are employed to estimate demand curves and elasticity.
Key steps to modeling the data include:
- Machine-Learning Models: Such as random forests or neural networks, which can handle large datasets and identify complex patterns.
- Segmentation Analysis: Different customer segments may have different price sensitivities. The assortment is segmented based on identified seasonality patterns.
- Regression Analysis: To identify the significance of relationship between the inputs such as price changes and the quantity demanded.
Data Modeling Done in Yieldigo
Within Yieldigo, after successful data alignment and cleaning, our software pre-models data using classification and clustering methods to group articles that demonstrate the same patterns.
- Yieldigo Application of Generalized Linear Models (GLM): Yieldigo’s software applies multilevel GLMs with log-link, a regression analysis model that can be used to study the relative change in an outcome variable. Fundamentally speaking, the effects Yieldigo software analyzes are predominantly multiplicative in nature (e.g. the same promotion having the potential for greater absolute impact on a bigger store, since its effect is not numerically additional, but rather scales with how popular or busy the store is on a regular basis).
- Yieldigo Usage of Bayesian Methods: Bayesian methods improve estimates for slow-moving inventory, namely the SKUs or items that sell less frequently or with limited data available. The final set of models used is thus the result of several layers of various modeling methods. As the process is based on machine-learning principles, it improves over time and adapts to changing environments automatically.
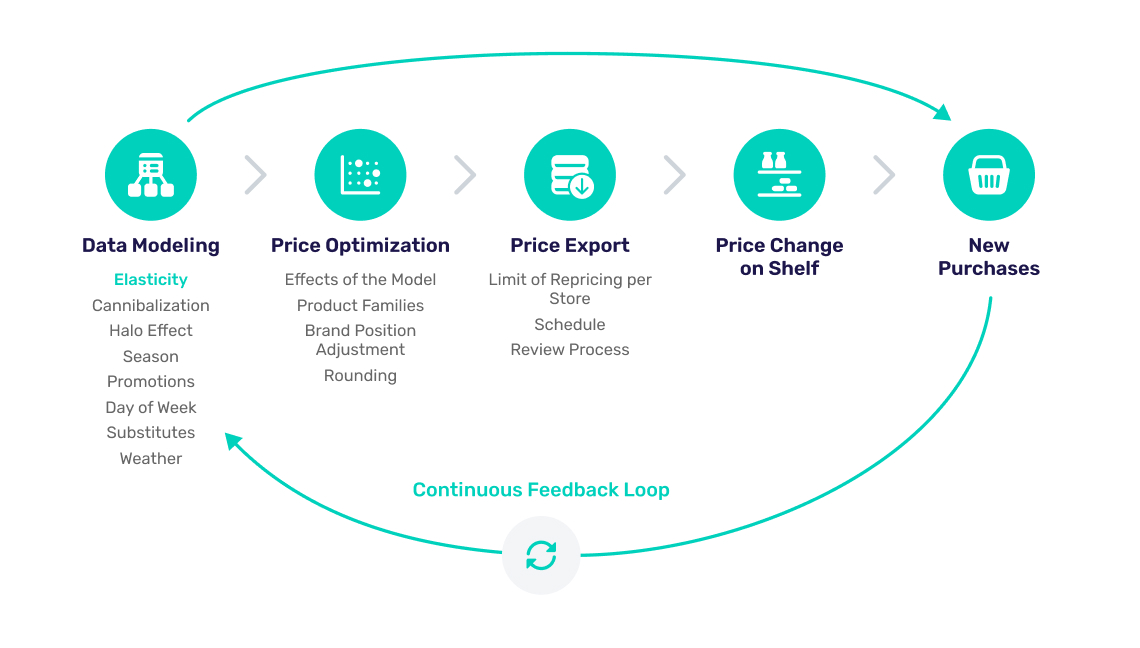
PART 2: The Continuous Feedback Loop
When referring to the Continuous Feedback Loop graphic above: Within Yieldigo price management software, the data modeling process is where we find our elasticities, amongst other related data modeling features, namely:
- Cannibalization and substitution effects
- Psychological impact of price thresholds (e.g. 9.99 → 10.00)
- Halo effects
- Seasonal demand fluctuation
- Effects of various promotions
- Sales trends per day of the week
- Weather impact on sales
Once again, we can see that your customer’s wallets are the primary source for all of these data modeling items. With all of the above in mind, let’s see how price elasticities are calculated from a mathematical and scientific point of view.
3. Elasticity Calculation
In terms of actual demand of any given product, price elasticity is calculated using demand models, otherwise known as PED (Price Elasticity of Demand). By definition, it is the ratio of percentage change in the quantity demanded of a product to the actual percentage change in its price.
The formula for price elasticity of demand upon which this is calculated is as follows:
On a technological level, the software automates this calculation in order to consistently reproduce the correct figures to achieve X result, in the following manner:
- Dynamic Calculation: PED is recalculated as new data comes in, ensuring the software always has up-to-date elasticity estimates.
- Scenario Analysis: The software can simulate how changes in price would impact demand and revenue.
In this way, depending on the data that our end-users input into their Yieldigo price management software, they render the results based on the desired goals their pricing teams set.
Instances When Price Elasticities Cannot be Calculated
It should be noted that price elasticities cannot be calculated in the following circumstances:
- When a new product becomes available/listed, and therefore there is no data yet available for it.
- It has had the same price throughout its entire sales history.
- Items with very low sales volume are often not possible to reliably estimate the price elasticity of since there is little data collected on them.
Therefore, technically it is true that elasticities cannot be calculated for all items. But, in order to remedy these cases of uncertain elasticities, Yieldigo’s solution performs clustering analysis to find groups of products with similar attributes and sales patterns, such as:
- Products in the same category, same brand, similar package size
- Similar seasonality patterns, promotions, trends, and so forth, as seen above in the Data Modeling box within the Pricing Process Part 2: The Continuous Feedback Loop diagram.
From these similarity clusters a conclusion about expected elasticity can be drawn even for products that can’t have their own price elasticity determined. And hence, this is why the argument that there are items for which elasticities cannot be calculated is, in fact, not 100 percent true. Clever usage of product grouping and other built-in price management tools that support the elasticity feature can be a rather precise adjustment to these potential price elasticity calculation issues. We will see this in greater detail further below.
4. Optimization Algorithms
Once the data integration has taken place and with the freshly calculated elasticity data in hand, price management software uses optimization algorithms to set prices for the following purposes:
- Revenue Maximization: Finding the price point where revenue is maximized given the elasticity.
- Profit Maximization: Considering costs to find the price point that maximizes profit.
- Competitive Edge: Using Dynamic Pricing to adjust prices in real-time based on demand, competition, and other factors in order to stay ahead of their specific retail market.
Price optimization is simply the process of searching for the best pricing solution given a specific set pricing goal.
Revenue maximization, profit maximization, and dynamic pricing are all essential to a retail business’s survival and success, both. Yet, the primary end goal of price optimization algorithms within any price management product is not to increase sales necessarily, but to save as much margin as possible by making the best pricing decisions, helping to maximize revenue, profit, and competitive prowess.
Price Optimization within Yieldigo
Price optimization is the process that uses the learnings of data modeling (which as we just saw above is the process that learns patterns of customer behavior) to achieve the following:
- Uses the pre-calculated models to predict outcomes of different scenarios
- Intelligently searches for the best possible solutions within any given constraint
- Runs automatically, at least once per day, as well as on-demand from the user interface
- Calculates prices for the whole assortment of a supermarket chain within mere minutes
Elasticities are a part of this optimization process that helps to deliver the above desired outcomes retail brands seek. The Daily feedback loop is where this process recurs again and again in order to keep on delivering optimally accurate price elasticity estimates, as well as the rest of the ML/AI optimization features within this cycle.
5. Implementation and Monitoring (The Daily Feedback Loop)
Once optimal prices are determined, the software helps implement and monitor pricing strategies:
- Integration with Sales Channels: Automatically updating prices across different platforms (e.g., online stores, POS systems, shelf labels).
- Performance Tracking: Monitoring sales and revenue to ensure pricing strategies are effective.
- Daily Feedback Loop: Continuously updating models and strategies based on real-time data and performance metrics.
The continuous process of learning and improving via the ML/AI engine of a price management product is where the real value lies. It is in this manner that pricing managers are able to stay on top of the latest pricing trends and suggestions in order to drive a successful pricing strategy, fully based on your data.
Yieldigo’s Daily Feedback Loop Interconnected across All Processes
Elasticities can be updated on a daily basis to provide the most up-to-date estimates, making them extraordinarily reliable and highly effective.
6. Advanced Features within Price Management Products that Support Price Elasticities
Price Management software leverages technological capabilities to automate and optimize the process of understanding and applying price elasticity. By integrating various data sources, employing sophisticated demand modeling, and using optimization algorithms, the software helps businesses make data-driven pricing decisions to achieve their financial goals.
Modern Price Management software includes advanced features that can be grouped as:
- Competitive Pricing Analysis: Using web scraping and other tools to monitor competitor prices and adjust strategies accordingly.
- Promotion Optimization: Evaluating the impact of discounts and promotions on demand elasticity.
- Personalized Pricing: Leveraging customer data to offer personalized prices based on individual price sensitivity (completely unrelated to price elasticities technologies, not offered in Yieldigo nor the majority of modern price management solutions).
- What-if Simulations: Providing upfront knowledge of pricing decisions on KPIs.
Different factors are analyzed on the product level using various features within Yieldigo’s software. The various continuous feedback loop tools offered within Yieldigo help reinforce the figures rendered by the price elasticity feature. In other words, by no means is the price elasticity feature an island of its own without support from other facets and figures rendered by the other tools that come with our software. This is why you absolutely can render elasticities for any product, even if there is not enough data available for one item in particular (and also by grouping products intelligently, the product is never alone in terms of some data that can reinforce its sales).
Not All Price Elasticities Are Made Equal
In order to understand why so much myth and uncertainty has loomed around price elasticities, it’s important to know that not every price management solution vendor offers technologies that render accurate price elasticities. Due in part to end-users not having competent pricing software equipped with a powerful ML/AI functionality, elasticities cannot be estimated with precision in order to be truly effective, in these cases. This has led to unpredictable and often mediocre results that have oftentimes put a stigma or ugly question mark on their reliability. In other words, myth has prevailed over reality in this case precisely because not all price elasticities are made equal – some price management products on the market are still not able to offer complete or accurate results, and this varies from vendor-to-vendor.
As such, competent price elasticity technologies often come under unfair scrutiny due to poor experiences end-users have had in the past with other inferior price elasticity technologies offered within some price management products.
Price Elasticities in Yieldigo
As we’ve seen, Price elasticities in Yieldigo are attached to a powerful ML/AI engine – paired with user data, it generates highly reliable price elasticities based on your data inputs. Our dedicated team of professionals help our clients implement our price management software, and also assist in integrating and cleaning their data to ensure that it’s reliable. As such, we have had nothing but very positive feedback from our users regarding our price management solution.
If you would like to learn more about how our price elasticities work and why our end-users rely on them, you can reach out to us and talk to our pricing expert.
4 Critical Price Elasticity Takeaways
Data modeling (and not some obscure black-box, “crystal ball” process) helps your retail organization capitalize on opportunities that can only be offered by intelligent pricing techniques such as price elasticities. As such:
- Price elasticities are based on your data as well as your customers’ purchases both past and present, continuously delivering data into your daily feedback loop. Remember, your elasticities come from your customers’ wallets.
- Supporting features within a powerful price management software itself help to deliver elasticities even when there is not enough data available, meaning that technically elasticities can in fact be applied and work well for any given SKU.
- Not all price elasticity technologies are built equally well – ensure that the price management product you are using is up to par with the latest technologies. If not, you are missing all of the fun (and also margins you could be saving).
- Your data is your only real limit. Assuming you’ve input reliable data (which is verified by Yieldigo’s implementation team if working with our software) and that your POS system is correctly sending the data it receives at every purchase to your data storage, your price elasticities and other ML/AI features are absolutely going to work to your benefit.
Want to see Yieldigo in action? No problem! Book a demo today and we will be happy to show you how our software can help your retail organization.